Read What You Want
Brain Stroke
When the blood flow to a section of your brain is blocked or decreased, brain tissue is deprived of oxygen and nutrients , resulting in a stroke. In a couple of minutes , brain cells start dying.
A stroke is a medical emergency that has to be treated right away.Brain damage and other consequences can be avoided if treatment is taken early.
Types of Strokes
Strokes are divided into 3 categories:

Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic Stroke is defined by a rapid loss of blood circulation to a portion of the brain , followed by a loss of neurologic function.
Acute ischemic stroke is more prevalent than hemorrhagic stroke and is caused by thrombotic or embolic blockage of a cerebral artery.
- Cerebral thrombosis occurs when fatty plaque within the blood vessels obstructs the flow of critical nutrients into the brain.
- Cerebral embolism is a kind of blood clot that forms around the heart and large arteries in the upper chest and neck.

Hemorrhagic Stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood artery in the brain breaks, causing bleeding. Blood harms brain cells as it presses against them. This can cause neurological problems.
Intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) and Subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) are two types of Hemorrhagic stroke .
- The most common type of hemorrhagic stroke is an intracerebral hemorrhagic stroke. It occurs when an artery breaks, causing the tissues around the brain to fill with blood.
- The occurrence of a subarachnoid hemorrhagic stroke is uncommon. It results in bleeding between the brain and the tissues that surround it.
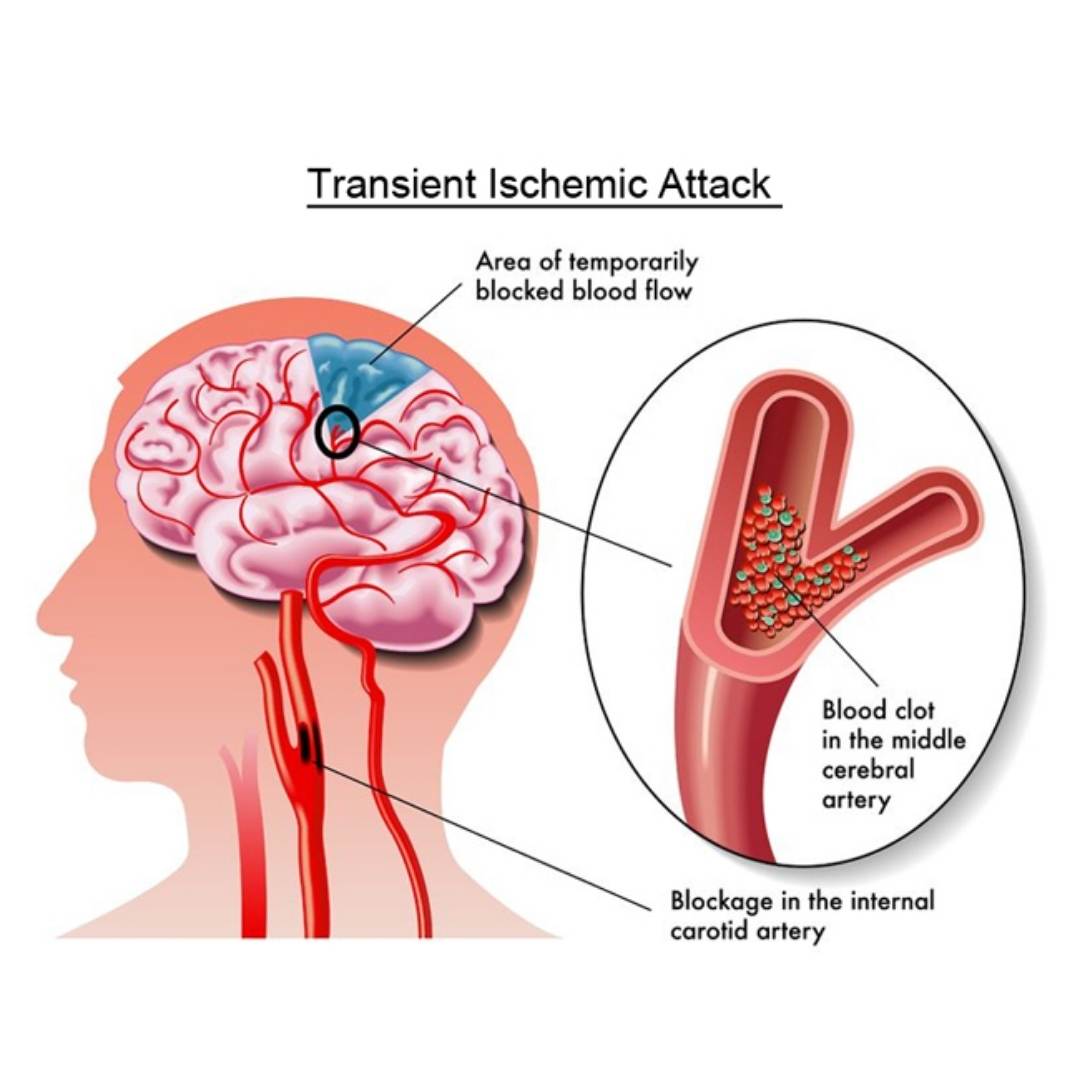
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
For a brief period of time, blood flow to a portion of your brain is interrupted. It’s also known as a ministroke. A transient ischemic attack (TIA) can signal the beginning of a full-blown stroke.
Approximately one-third of those who experience a TIA will go on to have a stroke within a year.
Although TIAs are brief and may not have long-term consequences, they should be treated as an emergency and treated as soon as possible.
Causes of Brain Stroke
Blood pressure is high: It’s possible that your doctor will diagnose it as hypertension which is the most common cause of strokes.
Tobacco: Smoking or chewing tobacco increases your risk of getting a stroke. The use of nicotine raises blood pressure. Cigarette smoke causes a fatty buildup in your major neck artery. It also makes your blood thicker and easier to clot. Secondhand smoke might have an impact on you as well.
Heart disease: Heart illness includes problems with cardiac valves as well as atrial fibrillation, or an irregular heartbeat, which is responsible for one of all strokes among the elderly.
Diabetes: People who have it are more likely to be overweight and have high blood pressure. Both increase the risk of a stroke. Diabetes affects your blood arteries, increasing your risk of a stroke. The damage to your brain is worse if you have a stroke when your blood sugar levels are high.
Exercise and weight: If you’re overweight, your chances of having a stroke increase. Working exercise every day can help you reduce your chances. Take a 30-minute brisk walk or engage in muscle-strengthening exercises such as pushups and weightlifting.
Medications: Some medications can increase your risk of having a stroke. Blood-thinning medicines, for example, which doctors recommend to prevent blood clots, can occasionally increase the risk of a stroke by causing bleeding. Hormone therapy, which is used to treat menopause symptoms including hot flashes, has been related to an increased risk of stroke in studies. Low-dose oestrogen used in birth control tablets may also increase your chances.
Age: A stroke can affect anyone, including babies in the womb. In general, as you get older, your odds improve.
Family: Strokes can be passed down through generations. It’s possible that you and your relatives have a family history of high blood pressure or diabetes. A hereditary condition that limits blood flow to the brain can cause some strokes.
Gender: Females are somewhat less likely to have a stroke than males of the same age. Women, on the other hand, have strokes later in life, making them less likely to recover and dying as a result.
Symptoms Of Brain Stroke
Signs and symptoms:
One or both eyes have vision problems: You may experience double vision or have blurred or darkened vision in one or both eyes.
Headache: A sudden, intense headache that is followed by vomiting, dizziness, or decreased awareness could be a sign of a stroke.
It’s difficult to communicate and understand what people are saying: You may be baffled, slur your words, or have trouble understanding communication.
Walking difficulties : It’s possible that you’ll trip or lose your balance. You may also experience dizziness or a loss of coordination.
Numbness or paralysis of the face, arm, or leg: Your face, arm, or leg may experience rapid numbness, weakness, or paralysis.Like, Attempt to raise both arms above your head at the same time. One side of your lips may sag as you try to smile.

Treatment of Brain Stroke
Physical examination: A doctor will ask about the person’s symptoms and medical history during a physical examination. Muscle strength, reflexes, feeling, eyesight, and coordination will all be examined. They may also take your blood pressure, listen to your carotid arteries in your neck, and look at the blood vessels in your eyes.
Blood Tests: A doctor may conduct blood tests to assess if there is a high risk of bleeding or blood clots, as well as to measure the amounts of specific substances in the blood, such as clotting factors, and to screen for infection.
Ct Scan: Haemorrhages, strokes, tumours, and other disorders in the brain can be seen using a series of X-rays.
MRI Scan: These create an image of the brain using radio waves and magnets, which a doctor can use to discover damaged brain tissue.
Carotid Ultrasound: An ultrasound examination of the carotid arteries may be performed by a doctor to examine blood flow and see if any narrowing or plaque is present.
Cerebral angiogram: To make the blood arteries in the brain visible on an X-ray or MRI, a doctor may inject a dye into them. This gives you a close-up look into the blood veins in your brain and neck.
Echocardiogram: This produces a comprehensive image of the heart, which doctors can use to look for any potential causes of clots in the brain.
Prevention
All strokes cannot be prevented by changing one’s lifestyle. However, many of these adjustments can make a significant difference in lowering your stroke risk.
The following are some of the changes:
Stop smoking
If you smoke, you can reduce your risk of stroke by stopping today.
Examine yourself on a regular basis
Consult your doctor about how often you should have your blood pressure, cholesterol, and any other conditions checked.
Consume alcohol in moderation
Drinking too much alcohol can elevate your blood pressure, which increases your risk of stroke.
Maintain a healthy weight
Obesity and being overweight raise the chance of having a stroke. Eat a well-balanced diet and engage in physical activity on a regular basis to help you manage your weight. Both of these methods can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.